What is the Direct Write-off Method for Bad Debts?
You can view aging reports, identify high-risk accounts, and prioritize follow-ups where they’re needed most. In this guide, we’ll explore effective methods, like the allowance and direct write-off approaches, and offer practical examples to simplify application. We’ll also highlight how InvoiceSherpa’s automation can streamline overdue invoice management and improve cash flow. Providing alternative repayment options, like installment plans or partial payment, can help customers facing temporary financial difficulties. This approach not only demonstrates goodwill but ensures the debt is addressed in a way that works for both parties.

Overview of GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles)

Because bad debts are recorded only when they become uncollectible, there can be a considerable time gap between the sale and the recognition of the bad debt expense. This delay can lead to financial statements that do not accurately reflect the company’s financial condition during the period in which the sales occurred. Bad debt expense is the loss that incurs from the uncollectible accounts, in which the company made the sale on credit but the customers didn’t pay the overdue debt. The company usually calculate bad debt expense by using the allowance method. With the direct write-off method, the company usually record Legal E-Billing bad debt expenses in a different period of those revenues that they are related to.
Direct Impact on Income Statement

Boost your confidence and master accounting skills effortlessly with CFI’s expert-led courses! Choose CFI for unparalleled industry expertise and hands-on learning that prepares you for real-world success. Let us understand the direct write-off method journal entries with the help of a couple of examples. These examples shall give us a practical overview of the concept and its intricacies. During periods of large write-offs, income can become significantly understated, while other periods may appear artificially profitable.
- If the transaction tells you what the new balance in the account should be, we must calculate the amount of the change.
- Bad debt recovery increases your net income by either reducing bad debt expenses or generating other income, depending on your accounting method and when you originally wrote off the debt.
- It offers more accurate financial reporting by matching expenses to the period when sales occur, following the matching principle in accounting.
- If you’re a small business owner who doesn’t regularly deal with bad debt, the direct write-off method might be simpler.
Aging Method
Accurate bad debt expense calculation is not only a regulatory requirement but also a fundamental aspect of sound financial management that supports the overall health and sustainability of the business. These disclosures help users of the financial statements understand the company’s approach to managing credit risk and the potential impact of uncollectible receivables on the financial results. By providing transparent and detailed information, companies enhance the reliability and comparability of their financial statements. This entry adjusts the allowance for doubtful accounts to the required level, ensuring that the financial statements accurately reflect the estimated uncollectible receivables.
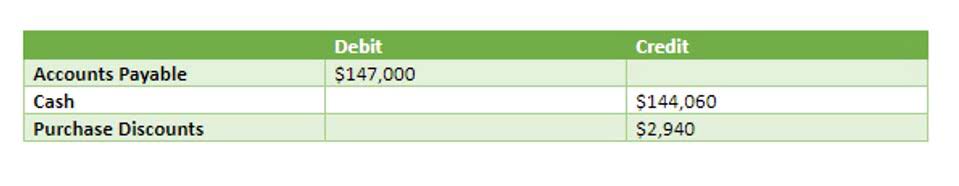
Comparing the Two Methods
The percentage of credit sales method is an income statement approach and estimates the required bad debt expense for an accounting period using a percentage of the credit sales made during the same period. The percentage of receivables method is a balance sheet approach, in which the company estimate how much percentage of receivables will be bad debt and uncollectible. In this case, the company usually use the aging schedule of accounts receivable to calculate bad debt expense. Regularly reviewing and adjusting bad debt estimates and the allowance for doubtful accounts ensures that the company’s financial statements accurately reflect the risk of uncollectible receivables. This ongoing process helps in maintaining the integrity of financial reporting and supports better decision-making. The Direct Write-Off Method is a straightforward approach to accounting for bad debt.

Useful for Low-Risk Receivables
By referring to these guidelines, sources, and further readings, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of how to calculate and manage bad debt expense under GAAP. These resources offer both theoretical knowledge and practical insights, ensuring that your accounting practices are robust and compliant. This entry removes the uncollectible receivable from the accounts receivable balance and reduces the allowance for doubtful accounts. This entry removes the uncollectible receivable from the accounts receivable balance and reduces the allowance for doubtful accounts accordingly. This entry adjusts the allowance for doubtful accounts to reflect the estimated uncollectible receivables based on the aging analysis. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are a set of accounting standards and guidelines that companies in the United States must follow when preparing their financial statements.
- Default in debt provided to a client or a third party can be a major pain point for businesses.
- The Allowance Method is a GAAP-compliant approach used to estimate and record bad debt expense.
- This method categorizes accounts receivable based on the length of time they have been outstanding and applies different percentages of uncollectibility to each category.
- If it is the allowance, you must then figure out how much bad debt to record in order to get to that balance.
- This process helps businesses reflect a realistic value of their accounts receivable, ensuring informed financial decisions.
Understanding Financial Statements Accounting Student Guide
The longer a debt has been outstanding, the less likely it is that the net sales balance will be collected. The aging method breaks down receivables based on the length of time each has been outstanding and applies a higher percentage to older debts. The contra-asset, Allowance for Doubtful Accounts, is proportional to the balance in the corresponding asset, Accounts Receivable.
- By proactively accounting for bad debts, businesses can better understand their true financial health and plan accordingly.
- Every time a business extends payment terms to a customer, that business is taking on risk.
- The direct write-off method waits until an amount is determined to be uncollectible before identifying it in the books as bad debt.
- Because the risk to the business is relative to the number of accounts and the amount of cash tied up in receivables, larger companies cannot take a “wait and see” approach to capturing potential bad debts.
- This method involves setting up an allowance for doubtful accounts, which acts as a contra asset on the balance sheet.
- Kristin is a Certified Public Accountant with 15 years of experience working with small business owners in all aspects of business building.
- Under the direct write-off method, recoveries reduce bad debt expense in the same period or appear as “other income” for prior periods.
- By mastering this method, you will be better equipped to handle receivables and ensure accurate financial reporting.
- Based on prior history, the company knows the approximate percentage or sales or outstanding receivables that will not be collected.
- This approach creates an allowance for doubtful accounts, reducing the net value of receivables on your balance sheet.
- The percentage of sales method is an income statement approach, in which bad debt expense shows a direct relationship in percentage to the sales revenue that the company made.
The Allowance Method is a GAAP-compliant approach used to estimate and record bad debt expense. This method involves creating an allowance for doubtful accounts, a contra-asset account that offsets accounts receivable on the balance sheet. The estimated bad debt expense is recorded through periodic adjustments based on historical data, current economic conditions, and management’s judgment. The Allowance Method involves estimating bad debts in advance direct write-off method and setting up an allowance for doubtful accounts. This method adheres to the matching principle, as it matches bad debt expenses with the revenues they help generate.